Factory pattern for Go tests
Nov 01, 2022
Most of Stormkit’s backend is written in Go. It’s a powerful language that has many benefits such as performance, scalability and it is considered one of the simplest languages to learn. It also has many built-in packages to solve common problems which ease development. Indeed, we decided not to use any ORM for our application layer but rely on the native database/sql package to communicate with the database. This is a simple solution but it may lead to some boilerplate code, especially while writing tests. To overcome this problem we came up with a pattern that we’re going to mention in this article.
The following diagram illustrates how our pattern looks like:
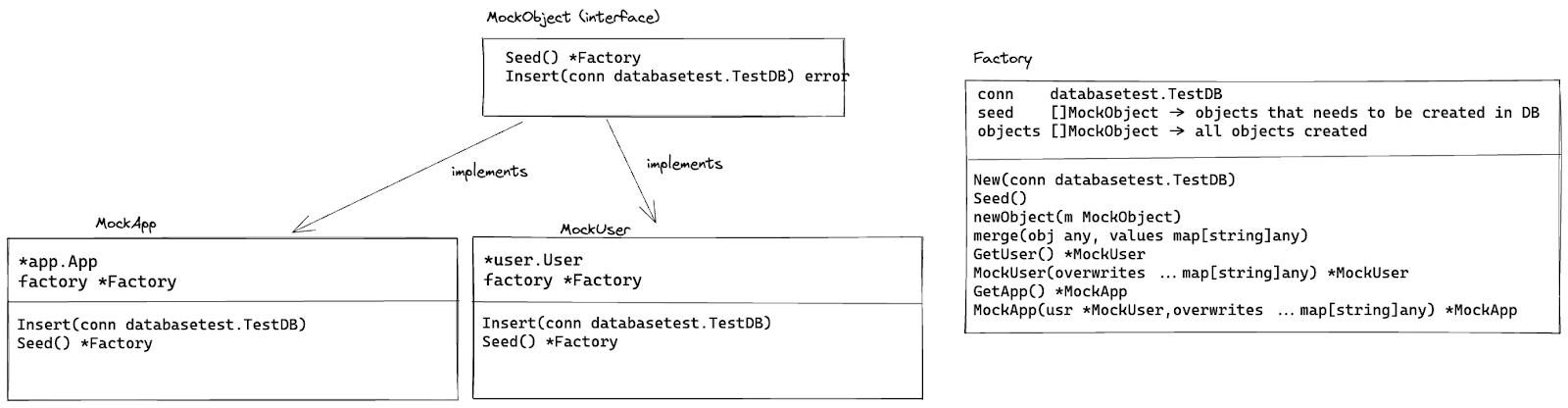
At first, it may seem confusing but the logic is actually pretty simple. However, before we dive into explaining this diagram, a little bit of context would be helpful to understand better our setup.
We represent objects using structs. For instance, here is how the App and User objects look like:
type App struct {
ID hide.Int64 `json:"id,string`
UserID hide.Int64 `json:"userId,string"`
Repo string `json:"repo"`
DisplayName string `json:"displayName"`
// ...more fields
}
type User struct {
ID hide.Int64 `json:"id,string`
Avatar null.String `json:"avatar"`
Email string `json:"email"`
DisplayName string `json:"displayName"`
// ...more fields
}
Now, let's assume we'd like to list the applications of a user. Each app needs to have an owner, which is the User object, and all other fields that are required. The following example shows how a test would look like without using the factory pattern. Think of this as a pseudo-code to keep things simple:
func TestListingApps(t *testing.T) {
// 1. spin up a fresh database
// 2. create mock objects
mockUser := &user.User{
ID: hide.Int64(1),
Email: "hello@stormkit.io",
DisplayName: "jdoe",
}
mockApp1 := &app.App{
ID: hide.Int64(1),
UserID: hide.Int64(1),
Repo: "github.com/stormkit-io/app-stormkit-io",
DisplayName: "app-display-name",
}
// ...mock more apps
// 3. insert user to the database
// 4. insert all apps to the database
// 5. Make a request to retrieve list of apps that belong to a user.
r := httptest.NewRequest("GET", "/apps", bytes.NewReader(payload))
w := httptest.NewRecorder();
appListHandler.ServeHTTP(w, r)
// We do use https://github.com/stretchr/testify for our tests
a := assert.New(t)
a.JSONEq(t, response.String(), expectedResponse)
}
This is quite a lot of boilerplate to write for a single test, imagine writing hundreds or thousands of them. By looking at the previous example, the next logical step was to abstract the mock objects into a separate package. We decided to call that package factory. The first version used to look like this:
package factory
func MockUser() *user.User {
return &user.User{
// fields
}
}
func MockApp(usr *user.User) *app.App {
return &app.App{
// fields
userID: usr.ID
}
}
So, using the first version of the factory package, the test above would look like this:
func TestListingApps(t *testing.T) {
usr := factory.MockUser()
app1 := factory.MockApp(usr)
app2 := factory.MockApp(usr)
// 1. insert usr, app1 and app2 to the database
// 2. make the request
// 3. write expectations
}
Now, this looks much better than the previous version, however, it's still not exactly what we were looking for. We were not satisfied from this package because:
- We had to create all objects in the hierarchy to create a mock object. In other words, to create a mock app, you first need to mock a user. To create a mock deployment, you first need to create a user, then an app, then an environment and finally you could create the deployment object.
- We still had to handle the database insertions.
- There was no simple way to overwrite object fields in a nice way. For instance, if we needed a user that had a different display name, we had to first create the mock object and then overwrite it. This approach becomes quite messy quickly, because once the object is created, if the code modifies it "somewhere in the code", it becomes harder to follow the code. Instead, we wanted to have the definition of the object when we created it.
So if we wanted to test a Deployment for instance, instead of creating all objects in the hierarchy, we wanted simply to do something like:
func TestDeployment(t *testing.T) {
// Create a new factory object and pass in the test database
f := factory.New(db)
// Create a new mock deployment object that finished successfully
deployment := f.MockDeployment(nil, map[string]any{
"ExitCode": 0,
})
// Insert all objects that the factory created for us (the user, app, environment and deployment objects)
f.Seed()
// 1. make a request
// 2. write expectations
}
So by creating a mock Deployment object, the factory package took care of creating the user, app and environment objects automatically for us. This is exactly what we were looking for.
Now, I guess it's time to dive in into the details and see how the factory package works behind the scenes.
The only method that the factory package exports is the New method, which returns a new Factory instance:
package factory
type Factory struct {
// fields
}
func New(conn databasetest.TestDB) *Factory {
// create a new factory instance and return it
}
Each time we setup a test that needs mock objects, we create a Factory object first. As we use testify suites for our tests, we have to do this only once when we setup our suite:
import (
"testing"
"github.com/stormkit-io/stormkit-io/lib/factory"
"github.com/stretchr/testify/suite"
)
type AppListSuite struct {
suite.Suite // This allows us using testify suites
*factory.Factory // We embed the factory object to the suite for easier access
conn databasetest.TestDB // The connection to the test database
}
func (s *AppListSuite) SetupSuite() {
s.conn = createDatabaseConnection()
}
func (s *AppListSuite) BeforeTest(_, _ string) {
s.factory = factory.New(s.conn)
}
So how does the factory package work? Basically, we do wrap each object with a MockObject interface:
package factory
type MockObject interface {
Seed() *Factory
Insert(conn databasetest.TestDB) error
}
type Factory struct {
conn databasetest.TestDB
seed []MockObject // A reference to objects that needs to be seeded
objects []MockObject // A reference to all objects created
}
Each MockObject has two public methods: Seed and Insert. Insert inserts the given object into the database, and Seed inserts ALL objects that were created so far. In reality, the Seed method is just a shorthand for the factory.Seed method, to allow chaining. Internally, the Seed method calls the Insert method to insert items into the database.
Every time we have to create a mock object, we define a new method for the factory. For instance, to create a MockUser object, we first create a definition for it:
type MockUser object {
*user.User
factory *Factory
}
and then we create the factory method:
func (f *Factory) MockUser(overwrites ...map[string]any) *MockUser {
usr := user.New()
usr.FirstName = 'Jane'
usr.LastName = 'Doe'
mockUsr := &MockUser{
User: usr,
Factory: f,
}
// Add the object to the list of objects to be seeded.
// Every time the `Seed` method is called, this list is being flushed.
f.seed = append(f.seed, mockUsr)
// Add the object to the list of objects, this list never gets flushed
// so the test has always access to the mock object.
f.objects = append(f.objects, mockUsr)
// Merge fields to be overwritten, more on this later.
for _, o := range overwrites {
merge(usr, o)
}
return mockUsr
}
Let's also take a look at the Seed method:
func (f *Factory) Seed() *Factory {
for _, object := range f.seed {
if err := object.Insert(f.conn); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
f.seed = []MockObject{}
return f
}
We simply iterate over the seed objects and insert all of them one by one. Now, what's cool about this approach is that each Mock* method contains it's logic internally. For instance, an App object, as described above, would need a User object to be created first. Let's take a look how we wrote the MockApp method:
// All we need is a mock user object, therefore return the first one found.
func (f *Factory) GetUser() *MockUser {
for _, object := range f.objects {
if _, ok := object.(MockUser); ok {
mock := object.(MockUser)
return &mock
}
}
return f.MockUser()
}
func (f *Factory) MockApp(usr *MockUser, overwrites ...map[string]any) *MockApp {
if usr == nil {
usr = f.GetUser()
}
// Just make sure that the user object is inside the database to obtain
// a valid user ID.
f.Seed()
// The rest is similar to the `MockUser` method.
mockApp := &MockApp{
App: &app.App{
UserID: usr.ID
}
}
// 1. populate fields
// 2. add mockApp to `f.seed` and `f.objects` lists.
// 3. return mockApp
return mockApp;
}
This approach allows us to call directly factory.MockApp method and do not worry about the hiararchy. Each test gets whatever it needs, without worrying about the underlying logic.
Finally, let's also take a look at the merge method. We do use the reflect package to overwrite field values:
func merge(obj any, values map[string]any) {
st := reflect.ValueOf(obj).Elem()
for k, v := range values {
f := st.FieldByName(k)
v := reflect.ValueOf(v)
f.Set(v)
}
}
This allows us to easily overwrite field values like:
func TestListingApps(t *testing.T) {
app := f.MockApp(nil, map[string]any{
"DisplayName": "my-other-display-name"
})
}
Conclusion
With this approach, the code is much simpler to read and writing tests are much more fun now. It was very beneficial for us, and we hope that it inspires you as well!
Stay safe :pray: