Database
Stormkit's Database feature provides each environment with an isolated PostgreSQL schema, complete with automatic schema migrations and secure credential management. This allows you to develop and deploy database-backed applications with confidence.
How it works
When you attach a database to an environment, Stormkit:
- Creates an isolated schema - A dedicated PostgreSQL schema (e.g.,
a123e456) for your environment - Generates secure credentials - Two separate database users with different permission levels:
- Migration user - Has DDL permissions (CREATE, ALTER, DROP tables) with strict resource limits
- App user - Has DML permissions only (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) for runtime operations
- Injects environment variables - Connection details are automatically available in your application
- Runs migrations (optional) - Executes SQL migrations from your repository during deployment
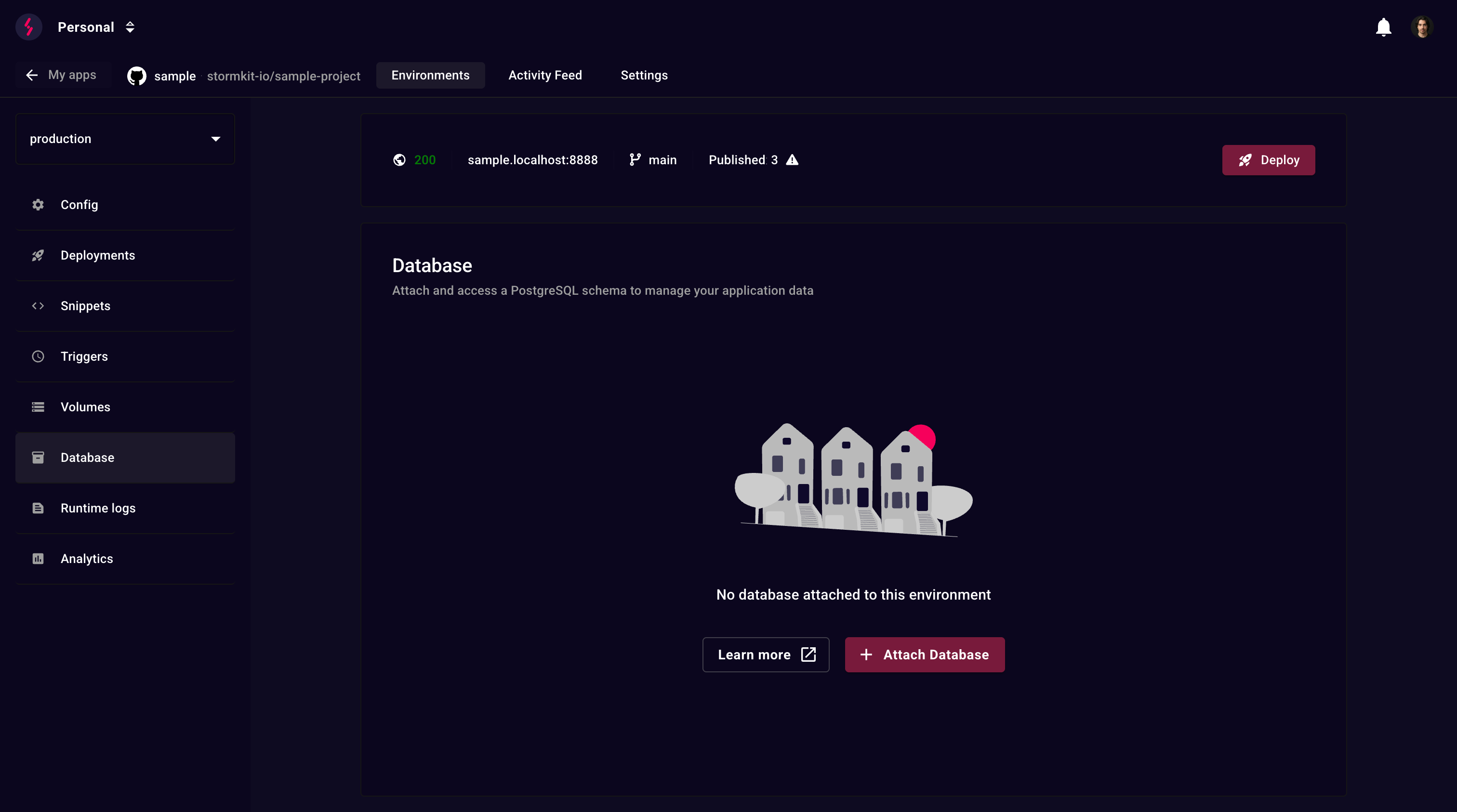
Attaching a database
Navigate to your environment's Database section and click Attach Database.
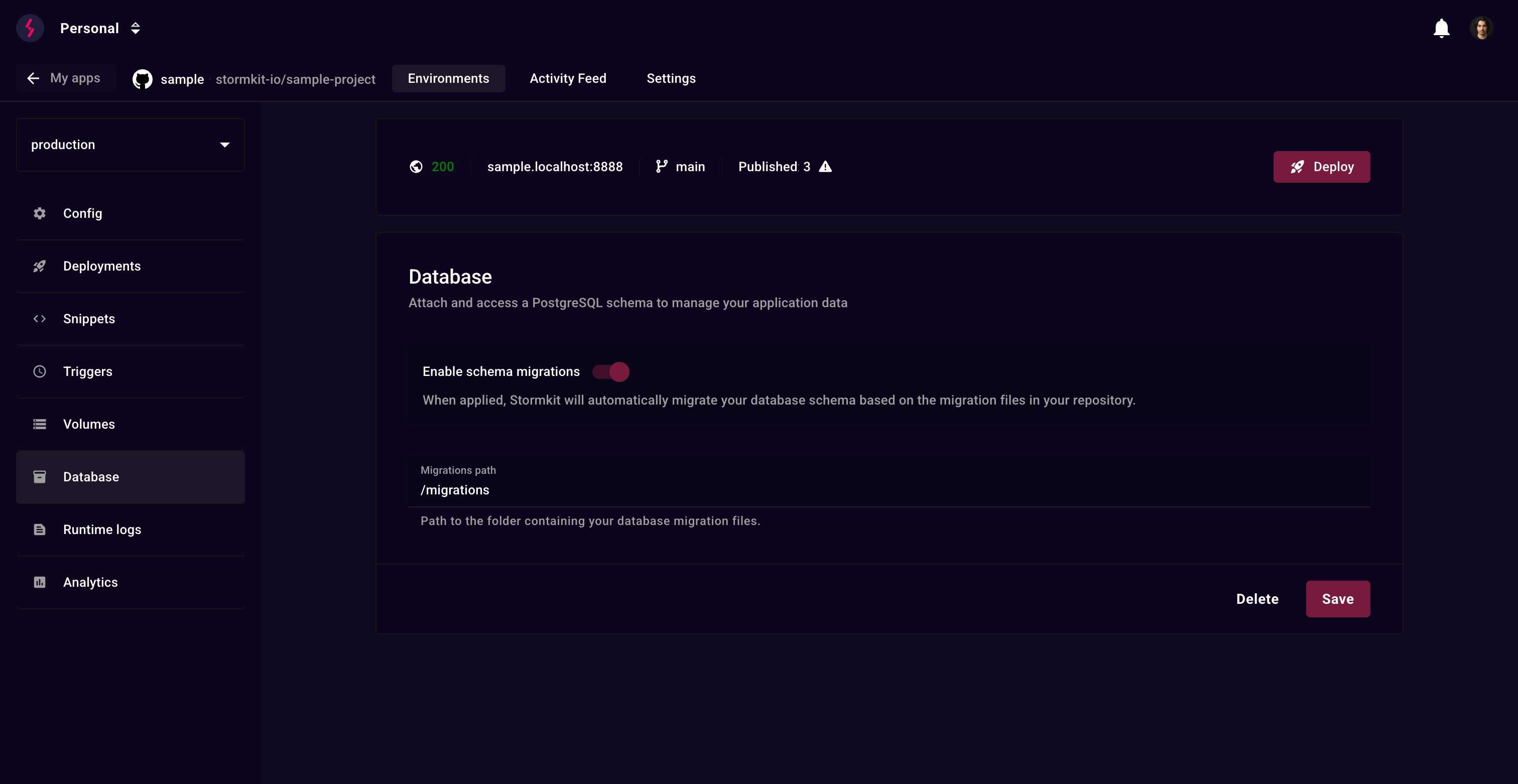
Automatic migrations
Enable schema migrations to automatically apply SQL migration files during deployment.
Why SQL-based migrations?
Stormkit's migration system is designed for simplicity and power:
- Fast iteration - Save a migration file and see database changes applied in milliseconds during deployment
- Roll-forward only - No rollback complexity to maintain. If something breaks, fix it forward with a new migration
- No learning curve - Write plain PostgreSQL syntax, no custom DSL or ORM to learn
- Full PostgreSQL power - Direct SQL execution means access to all PostgreSQL features: triggers, functions, custom types, extensions, and more
Configuration
- Enable the Enable schema migrations toggle
- Set the Migrations path (e.g.,
/migrations,/db/migrations)
Migration files
Place your SQL migration files in the configured path and deploy your application:
/migrations
├── 001_create_users.sql
├── 002_add_posts.sql
└── 003_add_comments.sql
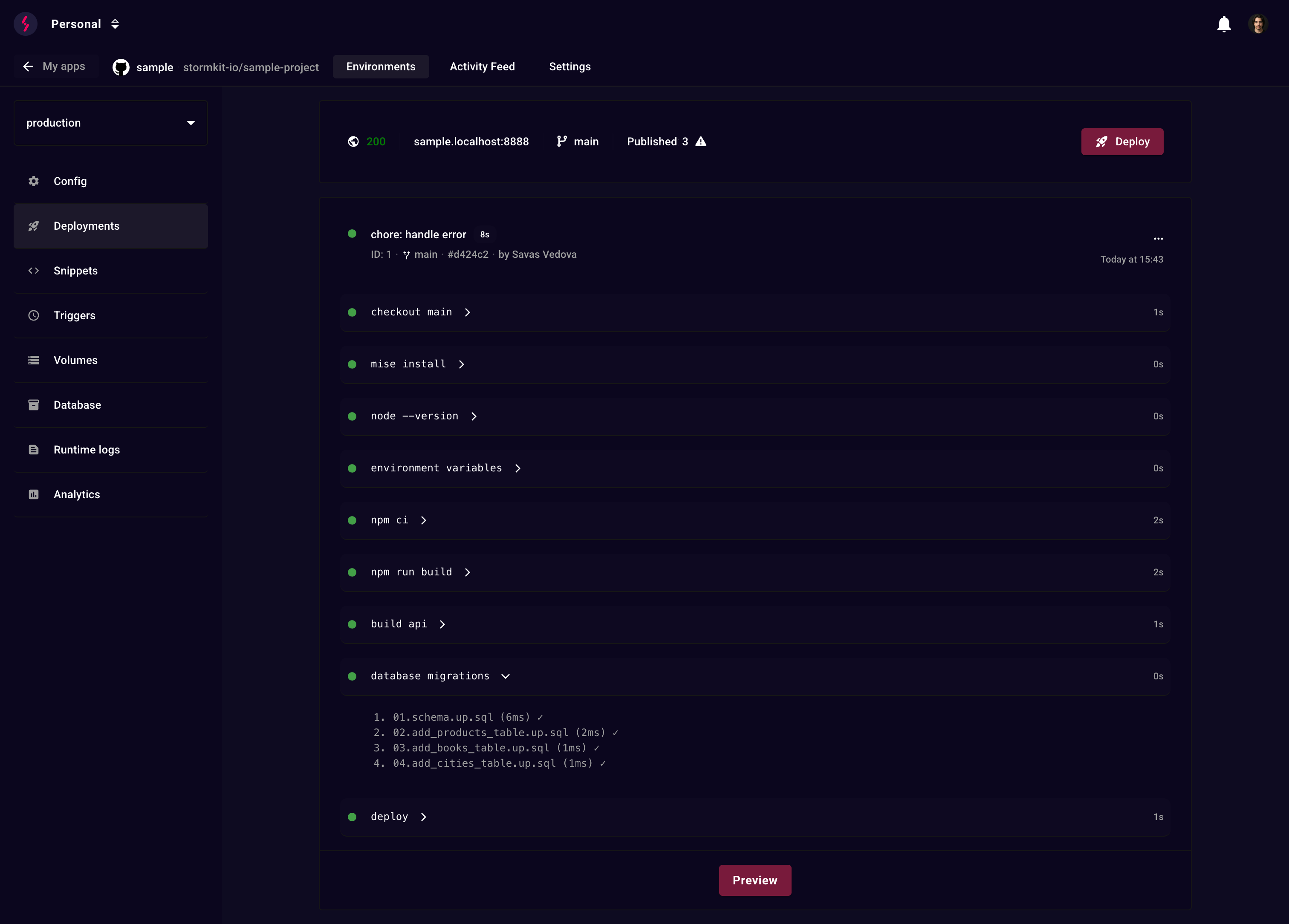
Important:
- Files are executed in alphabetical order - use numeric prefixes (001, 002, etc.)
- Each file is executed once per deployment
- Failed migrations abort the deployment
- If the content of a previously executed file changes, it is re-executed
- The migrations are executed only when environment's default branch is updated
Example migration file
-- migrations/001_create_users.sql
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
email TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT NOW()
);
CREATE INDEX idx_users_email ON users(email);
Environment variables
The following environment variables are automatically injected into your application:
DATABASE_URL=postgresql://user_name:secure_password@db_host:5432/db?options=-csearch_path=my_schema
POSTGRES_USER=user_name
POSTGRES_PASSWORD=secure_password
POSTGRES_HOST=db_host
POSTGRES_PORT=5432
POSTGRES_DB=db
POSTGRES_SCHEMA=my_schema
You can use these in your application:
// Next.js, Remix, etc.
const db = new Client({
connectionString: process.env.DATABASE_URL,
});
Security & permissions
Migration user
Used only during deployments with resource limits:
| Configuration Option | Value |
|---|---|
statement_timeout |
30s |
lock_timeout |
10s |
temp_file_limit |
100MB |
work_mem |
4MB |
idle_in_transaction_session_timeout |
60s |
connection limit |
1 |
Can do: CREATE/ALTER/DROP tables, indexes, and sequences within the schema
Cannot do: Access other schemas, create databases, modify roles, or access the file system
App user
Used by your running application with runtime limits:
| Configuration Option | Value |
|---|---|
statement_timeout |
15s |
lock_timeout |
5s |
temp_file_limit |
100MB |
work_mem |
8MB |
idle_in_transaction_session_timeout |
60s |
connection limit |
10 |
Can do: SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE on tables and sequences
Cannot do: ALTER/DROP tables, CREATE tables, or access other schemas
Deleting a schema
To delete a schema:
- Navigate to Database section
- Click Delete
- Confirm the deletion
Warning: This action:
- Drops the schema and all data permanently
- Removes both migration and app users
- Terminates active database connections
- Cannot be undone
Best practices
Migration files
- Use numeric prefixes or timestamps for ordering:
001_,002_,003_ - Make migrations idempotent when possible: Use
IF NOT EXISTS,IF EXISTS - Keep migrations small and focused on one change
- Test migrations locally before deploying
- Never modify existing migrations - create new ones to fix issues
Limitations
- PostgreSQL only - Other databases are not supported
- Single schema per environment - Each environment gets one schema
- Migration rollback - Rollbacks must be handled with new migration files